|
Acid phosphatase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphate esters by adding water under acidic conditions. It is widely distributed in various tissues and cells, playing crucial roles in numerous biological processes, including bone metabolism and cellular signaling. Isoenzymes of acid phosphatase share the same enzymatic function but exhibit significant variations in tissue distribution, chromosomal location, molecular weight, amino acid sequence similarity, protein length, and sensitivity to L(+) tartrate and fluoride. The accurate measurement of acid phosphatase activity is essential for understanding its physiological functions, diagnosing diseases, and monitoring therapeutic responses. |
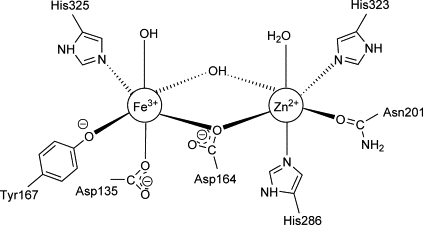
Prostatic acid phosphatase structure |
Applications of acid phosphatase activity assay
Clinical Diagnostics
Acid phosphatase levels in serum can serve as biomarkers for various diseases:
- Prostate Cancer: Elevated prostatic acid phosphatase levels may indicate prostate malignancy.
- Bone Disorders: Changes in total acid phosphatase levels can reflect bone metabolism abnormalities.
Reasearch applications
Acid phosphatase assays are widely used in cell biology to assess cell growth and viability, as they correlate well with cell number. They are particularly useful for:
- Evaluating effects of growth factors and cytokines on cell proliferation.
- Studying metabolic processes involving phosphate groups.