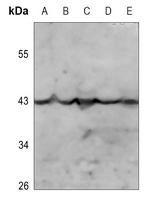
Application 
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P41145 |
| Other Accession | P33534 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 42645 Da |
| Gene ID | 4986 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | OPRK1; OPRK; Kappa-type opioid receptor; K-OR-1; KOR-1 |
| Target/Specificity | Recognizes endogenous levels of Kappa Opioid Receptor (pS369) protein. |
| Dilution | WB~~WB (1/500 - 1/1000) |
| Format | Liquid in 0.42% Potassium phosphate, 0.87% Sodium chloride, pH 7.3, 30% glycerol, and 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. |
| Storage | Store at -20 °C.Stable for 12 months from date of receipt |
| Name | OPRK1 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | OPRK |
| Function | G-protein coupled opioid receptor that functions as a receptor for endogenous alpha-neoendorphins and dynorphins, but has low affinity for beta-endorphins. Also functions as a receptor for various synthetic opioids and for the psychoactive diterpene salvinorin A. Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Signaling leads to the inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity. Inhibits neurotransmitter release by reducing calcium ion currents and increasing potassium ion conductance. Plays a role in the perception of pain. Plays a role in mediating reduced physical activity upon treatment with synthetic opioids. Plays a role in the regulation of salivation in response to synthetic opioids. May play a role in arousal and regulation of autonomic and neuroendocrine functions. |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein |
| Tissue Location | Detected in brain and placenta. |